Customer success is firmly entrenched in the SaaS business model. According to a 2020 study by TSIA, more than 90% of organizations had a dedicated customer success role in their company.
Nick Mehta, CEO and Founder of Gainsight, recently said, “Every single software company has a customer success program now. And it’s not just lip service anymore, where they put three or four people into the program. Many, many companies have hundreds and hundreds of Customer Success Managers trying to scale the business and drive net retention.”
While customer education didn’t gain the widespread recognition it deserved until relatively recently, it’s quickly gaining mainstream status, and the role of Customer Education Manager (CEMs) is becoming common.
Unfortunately, the lines between the two mission-critical functions—CEMs and CSMs—are blurred, leading to an unhealthy overlap leading to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and a subpar customer experience.
Let’s demystify these roles to answer some fundamental questions:
- How are CSMs and CEMs different?
- How are CSMs and CEMs the same?
- How can these functions work together to enhance the customer experience?
What’s a Customer Success Manager (CSM)?
A Customer Success Manager or CSM works with a set number of customers to ensure they have the tools and support they need to realize the value of a product. CSMs often act as guides, advisors, and advocates for their customers.
Key Responsibilities of a Customer Success Manager
- Customer onboarding: Responsible for the onboarding experience or familiarizing customers with the product to ensure a smooth start and low time-to-first-value (TTFV).
- Build relationships: Serve as the bridge between customers and the rest of the company, making it critical that they work to build relationships with their customers, understand their objectives, and develop success plans. Initial onboarding is essential, but the relationship often drives the most long-term lifetime value, product adoption, and retention.
- Ongoing support: Act as a source of support for customers. They’re available to answer questions, resolve issues, be strategic, and ultimately ensure customers realize product value beyond the onboarding process.
- Problem-solving: They anticipate potential challenges before they arise and address them before they become a point of friction—and potential churn—for customers. This often involves proactive outreach to mitigate risk and drive product adoption.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: With a deep understanding of individual customers’ needs and the company’s product, CSMs can drive revenue by identifying suitable opportunities
- Customer advocacy: Voice the needs and concerns of customers across the company, including to key internal stakeholders working in product, sales, and marketing, to ensure everyone’s aligned and working toward fulfilling the customer’s expectations.
Examples of Job Responsibilities for a CSM
Sr Customer Success Manager | Veracode
The Senior Customer Success Manager (Sr CSM) is responsible for building and maintaining strong relationships within assigned strategic accounts, ensuring high levels of customer satisfaction and recognition of ROI, leading to renewals and solution customer-led growth opportunities. The Sr CSM works closely with our customers alongside Sales, Renewals, Support, Security Consultants, and Product Management teams at Veracode to ensure our services are delivered successfully and meet customer expectations.
Customer Success Manager | Kandji
As a Customer Success Manager, you’ll be responsible for the success of our customers. As a Trusted Advisor with deep product knowledge, and empathy, you’ll understand customers’ business objectives and align them with product capabilities.
You’ll lead end-user training and enablement initiatives, conduct customer onboarding and business reviews, and serve as the “voice of the customer” in internal meetings. You’ll be responsible for ensuring retention, identifying new business opportunities, and driving high product usage, and value across our customer base.
Customer Success Manager | NielsenIQ
You will be responsible for managing the relationship of key account, Walmart, including: client objectives, growth strategy and engagement plan for a portfolio of NIQ Brandbank’s key Retailer clients. You will own every stage of the customer journey from implementation through to renewal and support the continued growth of our business.
You will act as the main point of contact for Walmart, dealing with everything from day-to-day queries through to strategic account planning and development, as well as establishing a network of contacts across the Walmart organization focusing on company-wide engagement with NIQ Brandbank.
What does all of this mean?
In one sentence: CSMs are primarily responsible for building and maintaining strong relationships with customers to ensure satisfaction, ROI, growth, and renewals.
Important Skills for Customer Success Managers
- Communication skills: CSMs often serve as the bridge between the customer and internal teams, making written and verbal communication skills critical.
- Empathy: A deep understanding of the customer’s perspective and needs is fundamental, allowing CSMs to build relationships, understand pain points, and provide personalized solutions.
- Problem-solving skills: Customers will face challenges, and CSMs need the ability to troubleshoot and offer effective solutions.
- Product knowledge: A comprehensive understanding of the product or service is key, enabling CSMs to explain functionality, answer questions, and ultimately drive product and feature adoption.
- Analytical skills: Whether it’s analyzing customer usage patterns or satisfaction metrics, a CSM must pull meaningful insights from data to inform outreach and strategy.
- Sales skills: While not a traditional sales role, CSMs can contribute to revenue growth through upselling and cross-selling. The ability to identify and act on these opportunities is a valuable skill.
- Customer service skills: At the heart of the role is a commitment to exceptional customer service, requiring patience, attentiveness, and the ability to make customers feel valued and understood.
In addition to these necessary skills, Bain and Company found additional motivations and personality traits the most successful CSMs share, including collaboration, a growth mindset, and an understanding of others. 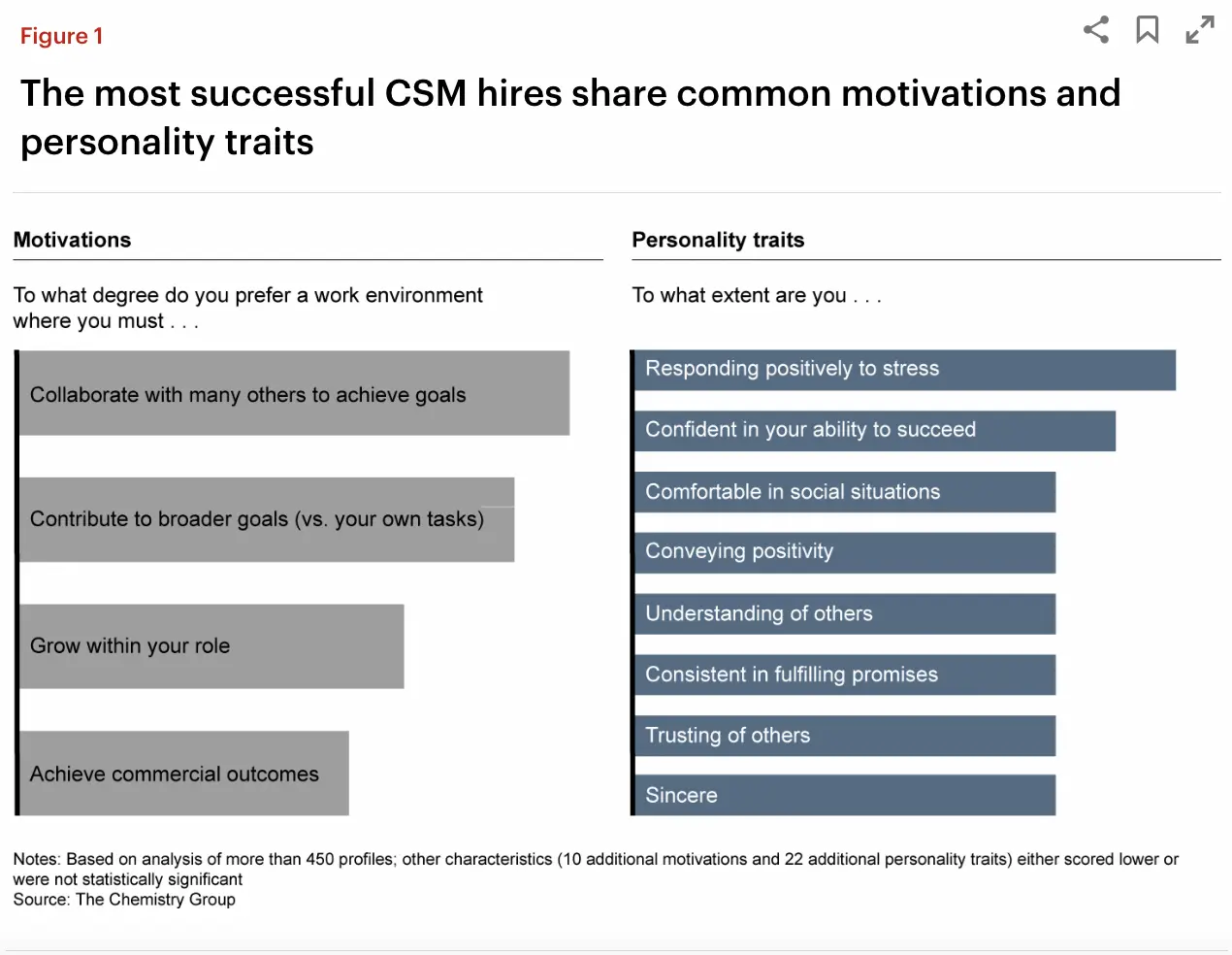
What’s a Customer Education Manager (CEM)?
Customer Education Managers, or CEMs, use educational resources, like learning paths and certification programs, to empower customers with the knowledge they need to get the most out of a product.
Key Responsibilities of a Customer Education Manager
CEMs share a lot of the same responsibilities as their counterparts in CS—drive product adoption, satisfaction, and renewals—but they do so in different ways. CEMs are primarily tasked with designing, developing, and delivering educational content to help customers maximize product value.
- Identify learning needs: Understand the customers’ learning needs, including the areas where they struggle and existing knowledge gaps.
- Design educational content: Responsible for creating engaging learning content that drives knowledge retention and product adoption.
- Develop training programs: Develop and execute training initiatives that help customers understand and use the product effectively.
- Deliver content: Ensure educational content reaches the customer in an accessible and understandable format.
- Evaluate program impact: Track and measure the impact of customer education. using feedback and engagement metrics to refine and improve their materials.
- Collaborate with other teams: Work with CSMs, product, and marketing teams to align content with product updates, marketing campaigns, and overall customer outcomes.
Examples of CEM Job Responsibilities
Customer Education and Support Manager | Proton.ai
Proton is looking for a Customer Education and Support Manager to join our fast-growing SaaS team! Reporting to our SVP of Customer, this key hire will be the foundational member of our scaled services team, managing most of the resources and content that helps our customers self-serve and thrive with Proton’s products.
It’s one of our company-level objectives to help our customers become more autonomous and successful using our product every day. You’ll be scaling our education and support services with a focus on small and mid-sized accounts. This includes both strategizing how to educate customers and also building the content and materials to support them.
Customer Education Program Manager | Samsara
Samsara’s Customer Education team continues to grow as we expand our enablement portfolio to ensure customers realize the full value of Samsara products across all phases of their journey. Your role as a Customer Education Program Manager will be cross-functional in nature, partnering with various teams and regions to develop emerging learning experiences aligned with our educational strategy, enabling you to experience multiple aspects of a hyper-growth company from within.
Education Enablement Manager | Siemens Digital Industries Software
The Education Enablement Manager is a strategic role in Siemens global academic program, managing a team collaborating with strategic stakeholders internally and externally to empower lifelong learners. This role leads key areas of enablement, including curriculum and credentialing, to deliver a shared value to academic institutions, Siemens customers and internal stakeholders.
*The listing also included this as one of the responsibilities: Improving the digital experience and engagement with Siemens technology and content for institutions, educators, and students.
Important Skills for Customer Education Managers
- Instructional design: Designing effective and engaging educational content across different mediums is key.
- Communication: Much like their CSM counterparts, CEMs need to be excellent communicators, capable of explaining complex product functionalities in simple and easy-to-understand ways.
- Analytical: Use data to understand how customers are engaging with their content, and then use these insights to improve the content and strategy.
- Technology skills: Familiarity with various learning technologies, including learning management systems (LMS), content management systems, and video editing software.
- Adaptability: Adapt quickly to changes and update their materials accordingly.
What does all of this mean?
In one sentence: A CEM is responsible for developing and implementing training that empowers customers to realize the full value of a product.
Customer Educaion vs. Customer Success: What’s the Actual Difference?
The positions may sound the same, but the differences are vast, including their responsibilities, which we’ve already discussed, but also their day-to-day activities and measures of success.
Let’s look at the primary differences:
Responsibilities
- CSM: Typically in charge of onboarding, providing strategic advice, and building relationships with customers.
- CEM: Typically in charge of developing and implementing training programs and initiatives that improve customers’ understanding and proficiency with a product.
Success
- CSM: Measured based on retention rates, upsell/cross-sell, customer satisfaction scores, and other key performance indicators (KPIs) directly tied to the customer’s success.
- CEM: Measured based on the effectiveness of their training programs, e.g., customer engagement with educational materials, improvements in product usage, or reductions in support tickets.
Customer Engagement
- CSM: Direct interaction with customers and often the primary point of contact.
- CEM: Work behind the scenes to develop training materials and programs that can be applied across the customer base.
Focus
- CSM: Play a big part in driving growth by identifying opportunities for upsells and mitigating churn.
- CEM: Focused on educational goals that equip customers with the knowledge they need to unlock a product’s full value.
So, How Are They the Same?
There are many fundamental differences between customer success and customer education. It should go without saying, then, that CSMs and CEMs are different, too.
That said, there are similarities, all revolving around enhancing the customer experience.
At the end of the day, CSMs and CEMs exist to understand the needs and challenges of customers and provide solutions that enhance their product experience.
They may do so in slightly different ways, but their primary goal is the same—the customer.
Ready to build a customer-centric organization? Learn more about Gainsight Customer Success and Gainsight Customer Education today.